The HHBSP provides a convenient framework for building QHS systems.
When you are ready to go ahead with product development, you will likely want to begin building the host and its guests in a framework that is tailored to your needs.
Download the HHBSP
The HHBSP board-agnostic framework (or BSP wrapper) is available from the QNX Software Center. If you want to use the HHBSP framework to build a QNX hypervisor system:
Download the appropriate HHBSP from the QNX Software Center. HHBSP archives are named according to the following pattern:
BSP_hypervisor-host_br-700_be-704_SVNrev_JBNbuild
where rev is the revision number, and build is the build number.
HHSBP archives for the QHS follow the same pattern, but include “safety” in the name; for example:
BSP_hypervisor-host-safety_br-700_be-704_SVNrev_JBNbuild
- Unpack your HHBSP archive to your workspace; for example, ~/qnx704/bsp/).
For the most up-to-date information about HHBSPs, see the Release Notes for your QHS or other QNX hypervisor package.
The HHBSP and board-specific BSPs
The Hypervisor Host BSP (HHBSP) is architecture- and board-agnostic; it works on any supported board. In order to be board-agnostic, the only board-specific components the HHBSP includes are some buildfiles.
Thus, after you have your HHBSP on your development host, you must download the board-specific BSP for your target board (e.g., the BSP for the Renesas R-Car H3) and place it in a convenient location. The default location is inside the HHBSP, in the images/host_bsp/ directory, but you can use another location as long as you set up your build environment accordingly (see “Configuring the build” in this chapter).
The descriptions below assume that you are using the HHBSP and the default locations for the board-specific BSP for the host, and for the architecture-specific BSPs for the QNX guests.
Contents of an HHBSP
When the host and guest BSPs have been downloaded and placed in the directories specified by the *_BSP_LOCATION variables, the HHBSP brings together into a single BSP directory structure the board-specific BSP for the hypervisor host itself, the BSPs for the guests, and the build and configuration files required to build the hosts and the guests.
The HHBSP provides:
- a directory structure where you can place the host BSP and the guest BPSs so that you can use a single make command to build the host, bring in the prebuilt guest files, and, if required, build the board-specific BSPs
- the source code files and the prebuilt binary for shmem-host, the host portion of the shmem-* demo application (download the guest portion (shmem-guest) separately in the guest BSP from the QNX Software Center)
- the source code files for the virtual watchdog devices for (wdt-sp805 for ARM and wdt-ib700 for x86)
- in the images/ directory, scripts, buildfiles, make files, etc. that allow you to build a hypervisor host, provided an appropriate board BSP is installed a location referenced by the BOARD_SPECIFIC_BSP_LOCATION variable (see “Configuring an HHBSP build”)
- a configuration file: configure.mk, where you must specify your target board, and where you may modify the locations of your host board-specific BSPs
- in the images/disk_config/ directory, configuration files, which you can use to configure the disk image you will transfer to your target board
- a generated/ directory, where the build process puts files it generates, including the final buildfiles it used to create the IFSs, so you can review them if you need to troubleshoot the build
Structure of an HHBSP
The figure below shows the HHBSP directory structure after the host BSP and the guest BSPs have been added to the default locations. Not all directories and files are shown; the diagram shows only the directories and files most relevant to building a hypervisor system.
When you have an HHBSP in your working directory, you will have there a typical QNX BSP directory structure, which will include the following:
- HHBSP root directory
- This directory has the standard BSP directories: images, install, prebuild and src; a Makefile; a source.xml file identifying the package (for the QNX Software Center); and a readme file (readme.txt) with information to identify the BSP.
The HHBSP is a framework. If you are using the default directories, you must place the board-specific BSP in the host_bsp/ directory, and the BSPs for any guest you will use in a directory you specify in the guest_data/ directory.
If you are using the default directories, you only need to specify the board type. If you are placing your host BSP elsewhere than the default location, you must configure variables to point to it (either your environment variables through the command line or the make variables by editing the configure.mk configuration file; see “Specify the component locations” in this chapter).
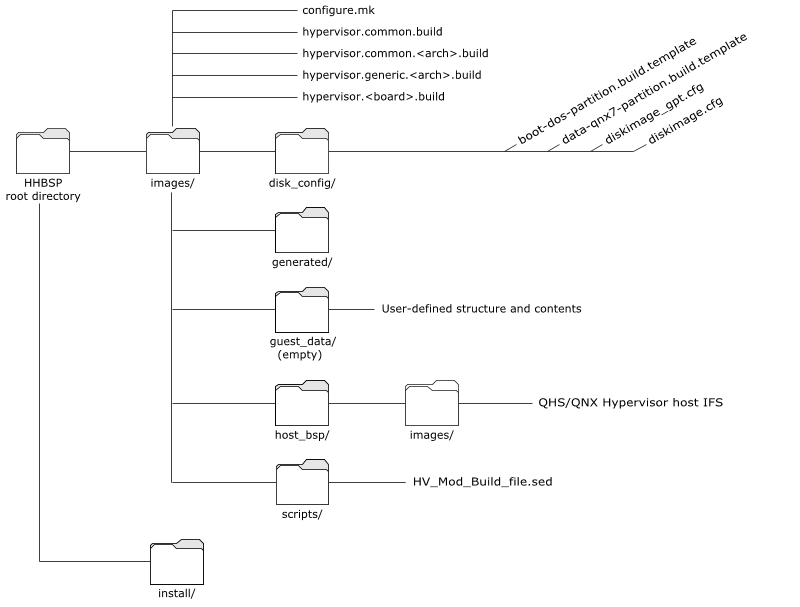 Figure 1. Partial view of the HHBSP directory structure.
Figure 1. Partial view of the HHBSP directory structure.Assuming that you are using the default locations, the images/ directory includes:
- disk_config
- A directory with the diskimage*.cfg and the *.partition.build.template files, which you can use to adjust the partition sizes in your disk image, and the contents of the filesystem in the image, for example, to speed up the boot time.
- generated
- Initially empty, this directory is a repository for files (e.g., the final buildfiles: hypervisor_FINAL_*.build), generated by the build.
- You can examine the files in these directories to learn more about how your build was made. Do not modify the files in this directory; they will be overwritten by the next build.
- guest_data
- An empty directory where you can create subdirectories for each guest BSP (e.g., qnx704/, qos21/, linux/).
- Set up the appropriate environment in each guest-specific directory and build the guest in that directory (see “Building guests” in this chapter).
- When you build your hypervisor system in the HHBSP, the build will include the contents of this directory at /guests/ in the disk image's QNX6 filesystem.
- host_bsp
- The host BSP directory. Extract the board-specific BSP for your hypervisor host into this directory. This BSP is the standard QNX SDP 7.0 or QOS 2.1 (as required) BSP used for the board.
- hypervisor-*.build files
- The hypervisor-common.build file has build instructions common to all architectures and boards.
- The hypervisor-generic.xml-arch.build files (where arch is either arm or x86) have architecture-specific build instructions common to all boards of the specified architecture; these are used when building a hypervisor system for a board not officially supported.
- The hypervisor-board.build files (where board is a board) have board-specific build instructions (see “How the build uses the buildfiles” in this chapter).
- scripts
- A directory with the HV_mod_Build_file*.sed scripts that modify buildfiles in the board-specific BSP directory to produce final, board-specific buildfiles for each each IFS that will be built (see “How the build uses the buildfiles” in this chapter).
- These final buildfiles will be placed in the generated/ directory.
Remember:
- The directories inside the host_bsp/ directory are added in only after you bring in the relevant BSPs.
- If you make changes to the board BSP buildfiles for your hypervisor host, make the changes in images/host_bsp/images/. Don't make the changes to the generated buildfiles in the generated/ directory, as these will be overwritten when you run your build.
For more information about the structure of QNX BSPs, see Building Embedded Systems in the QNX SDP 7.0 documentation.
Location of the IFSs after a build
When you run make to build your hypervisor system, the build will place the following in the images/ directory:
- a bootable disk image called hypervisor.diskimage with IFSs for the hypervisor host in the bootable partition
- a data partition with IFSs for the guests, as well as miscellaneous system files not needed at boot time; you can move files (e.g., buildfiles) out of the IFS to this partition to speed up the boot time
For more information, see “Building in the HHBSP” in this chapter.