Convert a node descriptor into a string
Synopsis:
#include <sys/netmgr.h>
int netmgr_ndtostr( unsigned flags,
int nd,
char * buf,
size_t maxbuf );
Arguments:
- flags
- Which part(s) of the Fully Qualified Path Name (FQPN) to adjust; see below.
- nd
- The node descriptor that you want to convert.
- buf
- A pointer to a buffer where the function can store the converted identifier.
- maxbuf
- The size of the buffer.
Library:
libc
Use the -l c option to qcc to link against this library. This library is usually included automatically.
Description:
The netmgr_ndtostr() function converts a node descriptor, nd, to a string and stores the string in the buffer pointed to by buf. The size of the buffer is given by maxbuf. If the string is too long to fit into the buffer, netmgr_ndtostr() truncates it. The function null-terminates the string.
A node descriptor is a temporary numeric description of a remote node. For more information, see the Qnet Networking chapter of the System Architecture guide.
The flags argument indicates which part(s) of the Fully Qualified Path Name (FQPN) to adjust. The following diagram shows the components for the FQPN, /net/my_node.qnx.com~preferred:
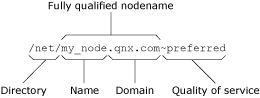 Figure 1. Components of a fully qualified pathname.
Figure 1. Components of a fully qualified pathname.The Fully Qualified Node Name (FQNN) is my_node.qnx.com.
The default string that netmgr_ndtostr() builds is the FQNN, plus the Quality of Service (QoS) if it isn't the default (~loadbalance). A process on another node can pass this string to netmgr_strtond(), and get a node descriptor that refers to the same node and QoS as nd.
To specify what to include in the string, specify a bitwise OR of the following bits in the flags argument:
- ND2S_DIR_HIDE
- Never include the directory.
- ND2S_DIR_SHOW
- Always build a pathname to the root directory (i.e., /) of the node
indicated by nd.
For example, calling:
netmgr_ndtostr(ND2S_DIR_SHOW, nd, buf, sizeofbuf)
on a node with a default domain of qnx.com using a nd that refers to a FQNN of peterv.qnx.com results in the string, /net/peterv.qnx.com/.
If Qnet isn't active on the node, and netmgr_ndtostr(ND2S_DIR_SHOW, nd, buf, sizeofbuf) has a nd of ND_LOCAL_NODE, then the string is /.
- ND2S_DOMAIN_HIDE
- Never include the domain.
- ND2S_DOMAIN_SHOW
- Always include the domain.
- ND2S_LOCAL_STR
- Display shorter node names on your local node. For example, calling:
netmgr_ndtostr(ND2S_LOCAL_STR, nd, buf, sizeofbuf)
on a node with a default domain of qnx.com using a nd that refers to an FQPN of /net/peterv.qnx.com results in a string of peterv, whereas a nd that refers to /net/peterv.anotherhost.com results in peterv.anotherhost.com.
- ND2S_NAME_HIDE
- Never include the name.
- ND2S_NAME_SHOW
- Always include the name.
- ND2S_QOS_HIDE
- Never include the quality of service (QoS).
- ND2S_QOS_SHOW
- Always include the QoS.
- ND2S_SEP_FORCE
- Always include a leading separator. For example, calling:
netmgr_ndtostr(ND2S_SEP_FORCE | ND2S_DIR_HIDE | ND2S_NAME_HIDE| ND2S_DOMAIN_HIDE | ND2S_QOS_SHOW, nd, buf, sizeofbuf)with a nd of ND_LOCAL_NODE results in a string of ~loadbalance. This is useful if you want to concatenate each component of the FQPN individually.
By combining the above bits in various combinations, you can extract all sorts of interesting information. For example:
- ND2S_NAME_SHOW
- A name that's useful for display purposes.
- ND2S_DIR_HIDE | ND2S_NAME_SHOW | ND2S_DOMAIN_SHOW
- A name that you can pass to another node and know that it's referring to the same machine (i.e., the FQNN).
- ND2S_DIR_SHOW | ND2S_NAME_HIDE | ND2S_DOMAIN_HIDE with ND_LOCAL_NODE
- The default network directory.
- ND2S_DIR_HIDE | ND2S_QOS_SHOW | ND2S_NAME_HIDE | ND2S_DOMAIN_HIDE with ND_LOCAL_NODE
- The default Quality of Service for the node.
Returns:
The length of the string including the NUL byte, or -1 if an error occurs (errno is set).
Errors:
- ENOTSUP
- Qnet isn't running.
Examples:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/netmgr.h>
int main ()
{
int nd1, nd2, nd3, len;
char path1[50] = "/net/dave",
path2[50] = "/net/karen",
buff[100];
nd1 = netmgr_strtond( path1, NULL);
if (nd1 == -1) {
perror ("netmgr_strtond" );
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
else {
printf ("Node id for %s is %d.\n", path1, nd1);
}
nd2 = netmgr_strtond( path2, NULL);
if (nd2 == -1) {
perror ("netmgr_strtond" );
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
else {
printf ("Node id for %s is %d.\n", path2, nd2);
}
nd3 = netmgr_remote_nd ( nd2, nd1 );
if (nd3 == -1) {
perror ("netmgr_strtond" );
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
else {
printf ("Node id for %s, relative to %s, is %d.\n",
path1, path2, nd3);
}
len = netmgr_ndtostr ( ND2S_DIR_HIDE | ND2S_DOMAIN_SHOW |
ND2S_NAME_SHOW | ND2S_QOS_SHOW, nd1, buff, 100 );
if (len == -1) {
perror ("netmgr_ndtostr" );
}
else {
printf ("Node name for %d is %s.\n", nd1, buff);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classification:
| Safety: | |
|---|---|
| Cancellation point | Yes |
| Interrupt handler | No |
| Signal handler | Yes |
| Thread | Yes |