The more time it takes to boot your base system (IPL, kernel, Core OS), the more time that it takes to start Screen.
Therefore, you must consider how to optimize the boot time for your base system.
Generally, after your system boots, a boot script runs to start device drivers, start services, and run applications. For more details about the system startup sequence, see About the System Startup Sequence.
Areas in the bootup sequence where time can be optimized
There are areas on your system that you can optimize. It's a good idea to have a good understanding of the boot optimization strategy for Screen before you dive in to the techniques. In general, Screen is optimized to start quickly on a system.Remember that not all optimization techniques are applicable to all systems. If your system doesn't have a GPU or a display, refer to optimization techniques that aren't associated with using a GPU or displaying content.
It's important to mention that this process of going through the following areas isn't linear, but best done in an iterative manner. For example, you might be able to further optimize your configuration file after you optimize your splash screen application.
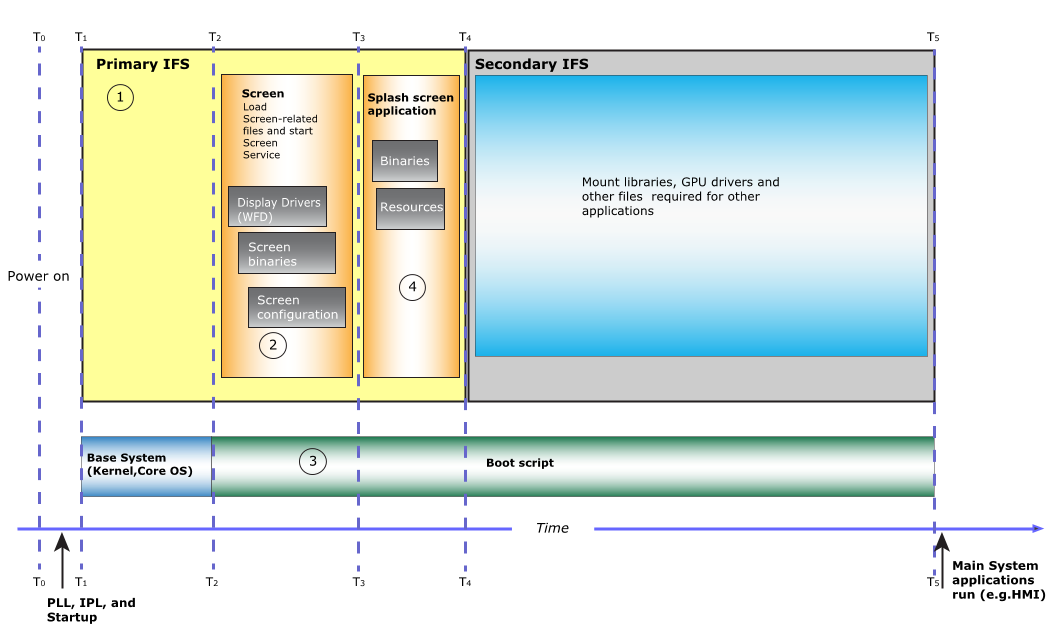
Figure 1. Areas that can be optimized.
- 1. Configure your system to have a primary and a secondary IFS (image filesystem)
- We recommend that you make the IFS as small as possible. If you have many files that need to be loaded into RAM, split the IFS into a primary and a secondary IFS. The primary IFS should have only the minimum files and libraries required to boot the system, to start Screen, and to start any applications you've included in the primary IFS (e.g., a splash screen application). It's important to remember that you require a secondary IFS only if files need to be loaded into memory; otherwise, you can put the files into the filesystem. For more information about creating a primary and secondary IFS, see the Configure a Primary and Secondary IFS on the System chapter.
- 2. Optimize the Screen configuration file
- To potentially reduce the time it takes for the Screen service to come up, you should remove any unnecessary parts from the graphics.conf file. For more information, see the Optimize the Screen Configuration File chapter.
- 3. Optimize your boot script
-
In your boot script (which is generated and configured in the script section of the buildfile that comes with your hardware platform's board support package (BSP)), run the minimal services, and then start Screen.
For systems with displays, you might want to provide a visual cue to indicate that the system is coming up or is in the process of coming up. For example, you might want to show content from a camera while the other components of your system initialize and start. In the boot script, you should start Screen, and then immediately start your splash screen application. You might also need to load any libraries your splash screen application depends on or start device drivers required for your content to show. After the boot script finishes, control is usually passed to a main system application, such as an HMI (human machine interface).
For more information, see the Optimize the Boot Script chapter.
- 4. Optimize the splash screen application
- Most of the optimizations occur in the implementation of your splash screen application.
You should try to use
software rendering
instead of hardware rendering. Much of the time that you can save can directly be attributed
to what resources and features your splash screen application demands from
Screen. For example:
- You can reduce the libraries that Screen dynamically loads if you use software rendering to draw an image.
- You can load an image in memory rather than read an image from a file (e.g., hard code your image as an array in your application).
- For more information, see the Optimize the Splash Screen Application chapter.
If you run other applications that also use Screen to display content, we recommend that you use the same techniques to optimize all applications as described in the Optimize the Splash Screen Application chapter.
Screen boot optimization strategy
By default, Screen is optimized to start quickly and uses as few system resources as possible. Screen loads resources and starts device drivers only when necessary. As a result of this, the timing for subsequent calls that require the same device driver is shorter than the first because the device driver is already running.
There are several ways that you can implement your system to help it start faster. In the following diagram, the green oval on the right lists the important boot optimization techniques that decrease startup time while those listed in the red oval on the left, are the non-recommended techniques (although ones that you might need to use due to system requirements) that typically increase startup time.
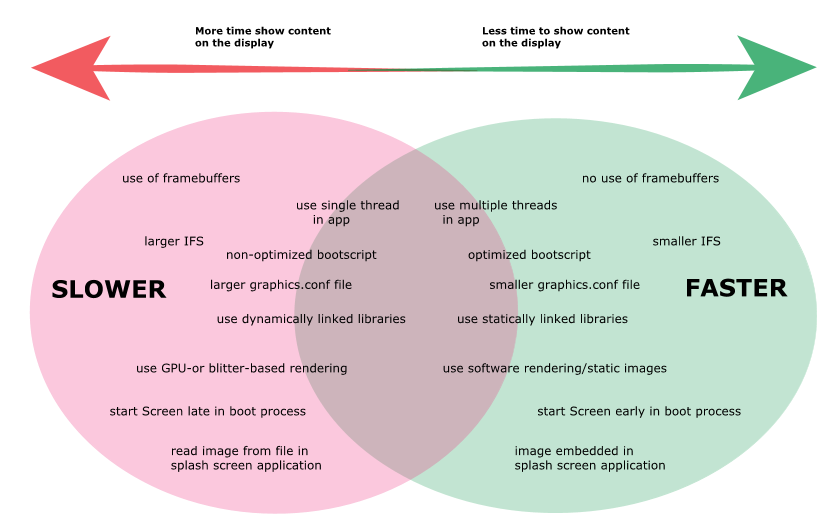
Figure 2. Impact of boot optimization techniques
If your system has displays and a GPU, it's important that you consider how to implement your splash screen application. Your implementation will often use at least the display driver, but if your splash screen application requires more device drivers to start, it will increase the time required for your content to show on a display. For example, if your splash screen application uses OpenGL ES hardware rendering (not recommended), additional device drivers are started, which increases the time for content to show on the display.
The use of framebuffers or starting Screen late in your system can significantly increase the time it takes to show content on the display. Conversely, not using framebuffers and starting Screen early in the boot process can significantly reduce the time it takes to show content on the display.
The previous diagram also shows how some techniques can have a larger impact than others to decrease or increase the startup time (which also impacts the time to show content on the display). For example, if you start Screen early in the boot process or remove the need to use framebuffers in your application, those techniques are more effective for reducing the time as compared to techniques, such as a reducing the size of the graphics.conf file or using statically linked libraries. If you had to choose a technique to focus on, choose the ones that are suitable for your system and applications, while giving the greatest benefit.
Hardware considerations when working with Screen
- For input devices, such as a mouse, don't enable the mouse cursor because it causes a framebuffer to be created, which increases the time it takes to show content on the display. If your system requires any input (other than touch input), you should start the hid device drivers. With respect to touch input, we recommend that you start the mtouch driver after your splash screen application runs. For example, if your system uses a mouse as input, you should start the hid driver before the Screen service, but don't show the mouse cursor.
- If your display or monitor is connected to your hardware via an output cable, such as an HDMI cable, the device driver might have a longer detection phase than you expect, which increases the time it takes to show content on a display. For that reason, it's better to use an attached device or a device driver that doesn't have a detection phase.