Valgrind Memcheck tracks all allocated heap blocks so it can find memory leaks when the program terminates. The tool writes the leak details into the analysis results, which the IDE then parses to display leak information.
The IDE switches to the QNX Analysis perspective. If necessary, the IDE first builds the binary before uploading it to the target. To analyze the application, the IDE instructs Valgrind to execute the uploaded binary with Memcheck instrumentation. Then, it creates a new session for storing the Valgrind results; this session is displayed in the Analysis Sessions view. When the program terminates, Valgrind writes the results to a log file, which the IDE copies into the directory for the new session.
The memory error details are listed in the Valgrind view.
All error summaries contain the Valgrind icon (![]() ) followed by a descriptive message and the PID of the Valgrind process.
On the left of the icon, you can click the arrow to display a stack trace of where the error was detected.
The depth of the displayed call chain is determined by the Callers in stack trace field in the
General Options tab.
) followed by a descriptive message and the PID of the Valgrind process.
On the left of the icon, you can click the arrow to display a stack trace of where the error was detected.
The depth of the displayed call chain is determined by the Callers in stack trace field in the
General Options tab.
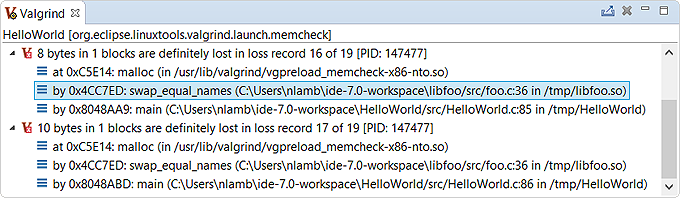
The stack traces should include location information for lost blocks allocated within functions of shared libraries. If you don't see this information, you must manually configure the loading of debug symbols.
If you double-click a trace line that has source file information, the IDE opens the source file at the indicated line. This feature lets you quickly find where a lost block was allocated.