The following describes a configuration for a virtio-net vdev for a node in a guest communicating with a devnp-vdevpeer-net.so driver in the hypervisor host.
The figure below illustrates a peer-to-peer connection using a virtio-net vdev in a guest and the devnp-vdevpeer-net.so io-pkt-* driver running in the hypervisor host (see devnp-vdevpeer-net.so in the “Utilities and Drivers Reference” chapter).
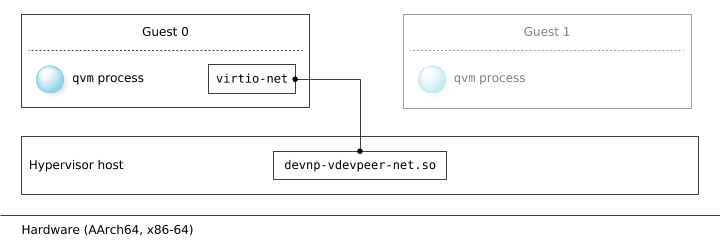 Figure 1. Guest-to-host communication using the virtio-net vdev to a
peer node provided by the devnp-vdevpeer-net.so
io-pkt-* driver.
Figure 1. Guest-to-host communication using the virtio-net vdev to a
peer node provided by the devnp-vdevpeer-net.so
io-pkt-* driver.The following shows the virtio-net vdev configuration in the *.qvmconf file for a VM (qvm process instance) hosting the guest, along with the io-pkt-* -d vdevpeer-net driver startup options that will enable the hypervisor host to connect to a node in the guest, and the instructions for enabling the interface.
Configure a virtio-net vdev
For a QNX Neutrino 7.0 guest on an ARM board, configure a virtio-net vdev in the VM as follows:
system qnx7-arm-guest ... # The loc and intr gic options are for ARM only. The guest # will see the virtio-net vdev as a memory-mapped I/O device # at the specified location. vdev virtio-net loc 0x1c0c0000 intr gic:40 mac aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa name p2p peer /dev/vdevpeers/vp0 peerfeats 0x3
where:
- qnx7-arm-guest
- The guest system name, also specified by the vdevpeer peer option: peer=/dev/qvm/qnx7-arm-guest/p2p.
- loc 0x1c0c0000
- The base address of the device registers.
- intr gic:40
- The interrupt number of the current virtual device (see “Common vdev options” in the “Virtual Device Reference” chapter).
- mac aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa
- The locally-assigned MAC address of the node in the guest.
- name p2p
- The name of the node in the guest, also specified by the vdevpeer peer option (peer=/dev/qvm/qnx7-arm-guest/p2p).
- peer /dev/vdevpeers/vp0
- The path to the node in the host, also specified by the vdevpeer bind option (bind=/dev/vdevpeers/vp0).
- peerfeats 0x3
- The VirtIO Network feature bits supported by the peer (see “Using the peerfeats option” in the “Virtual Device Reference” chapter's vdev virtio-net entry).
Start vdevpeer-net
Start io-pkt-* in the host, specifying the following for the vdevpeer-net driver:
io-pkt-v6-hc -d vdevpeer-net \ peer=/dev/qvm/qnx7-arm-guest/p2p,bind=/dev/vdevpeers/vp0,mac=a0b0c0d0e0f0
where:
- peer=
- The path to a virtio-net vdev in the guest, inside the /dev/qvm/ directory. The remainder of the path is specified by the virtio-net vdev system option for the guest's directory (qnx7-arm-guest), and, inside this directory, the node in the guest, specifed by the vdev's name option (p2p).
- bind=
- The path to the node in the host, inside the /dev/vdevpeers/ directory. In this case the default prefix vp is used for node zero (vp0).
- mac=
- The MAC address for the node in the hypervisor host.
Enable the interface
Finally, assuming that you have already enabled an interface on the host. For example:
ifconfig vp0 up ifconfig vp0 192.168.1.1
you must now enable the interface on the guest and assign it a static IP address in the same subnet as the host. For example, for a QNX Neutrino OS guest:
ifconfig vt0 192.168.1.2
where vt0 is the name of the interface on the guest, vp0 is the peer-to-peer interface on the host, and 192.168.1.2 is an address in the same subnet as the host.
For a Linux guest:
sudo ifconfig enp0s3f0 up sudo ifconfig enp0s3f0 192.168.1.2
where enp0s3f0 is the peer-to-peer interface, and 192.168.1.2 is an address in the same subnet as the host.
If peerfeats bit 1 (one) is set for the peer interface on the guest, you need to make sure that checksum settings for the interface on the host matches the checksum settings for the interface on the guest; for example, to disable checksums for TCP/IP and UDP on the node, configure it as follows:
ifconfig vp0 -tcp4csum -udp4csum -udp6csum -tcp6csum
What the guest sees
The guest sees network interfaces with vt or enp prefixes. It isn't aware of any peer naming, so you must define how a vt and enp interface is mapped to a peer. MAC addresses provide confirmation of the mapping.